 1 · Environment
1 · EnvironmentAcid Rain
Causes: Burning fossil fuels, industrial emissions.
Consequences: Forest damage, water pollution.
Each card includes a definition, key causes and consequences. Enjoy the website :)
 1 · Environment
1 · EnvironmentCauses: Burning fossil fuels, industrial emissions.
Consequences: Forest damage, water pollution.
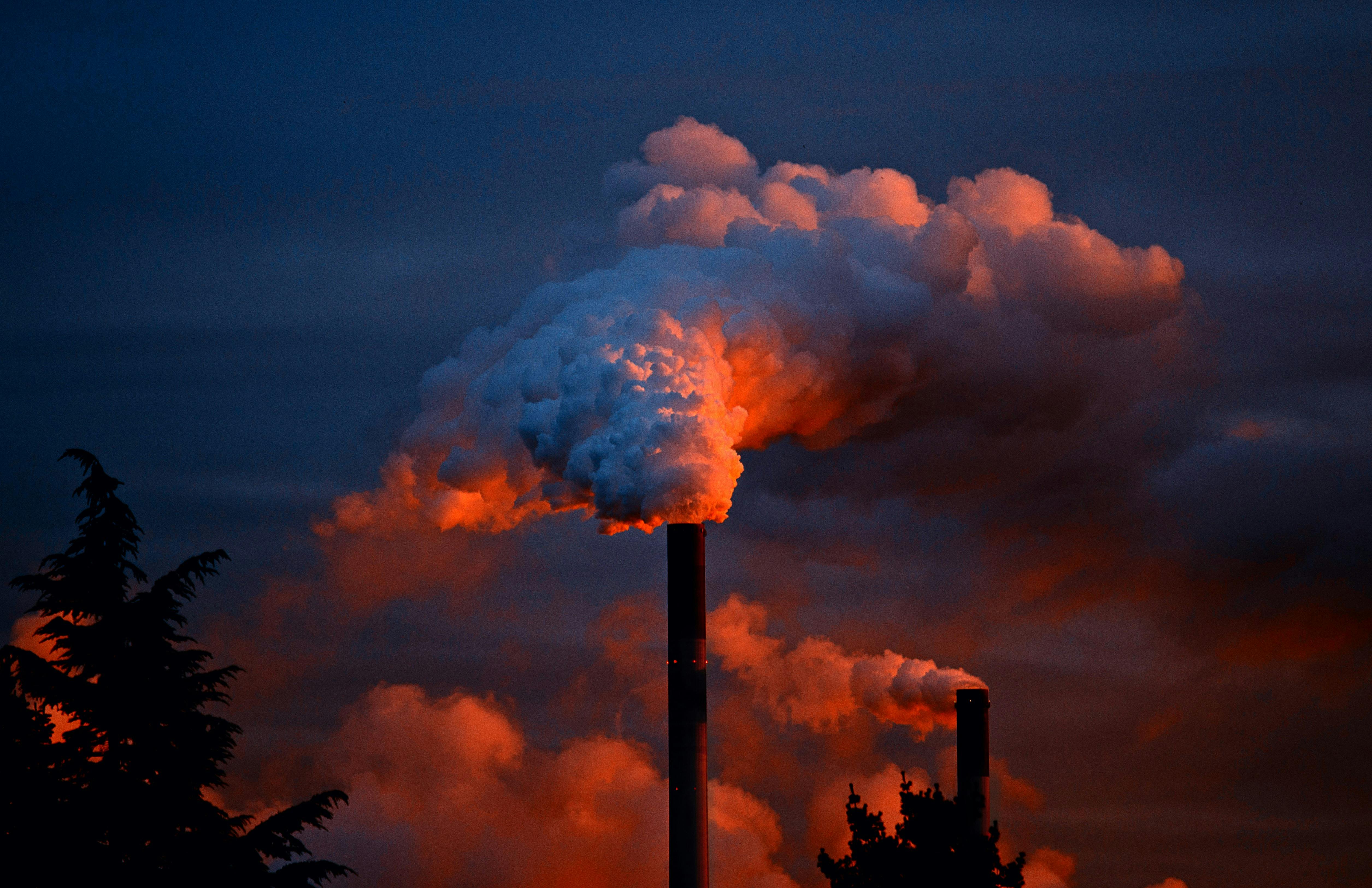 2 · Environment
2 · EnvironmentCauses: Transportation, factories.
Consequences: Respiratory diseases, climate change.
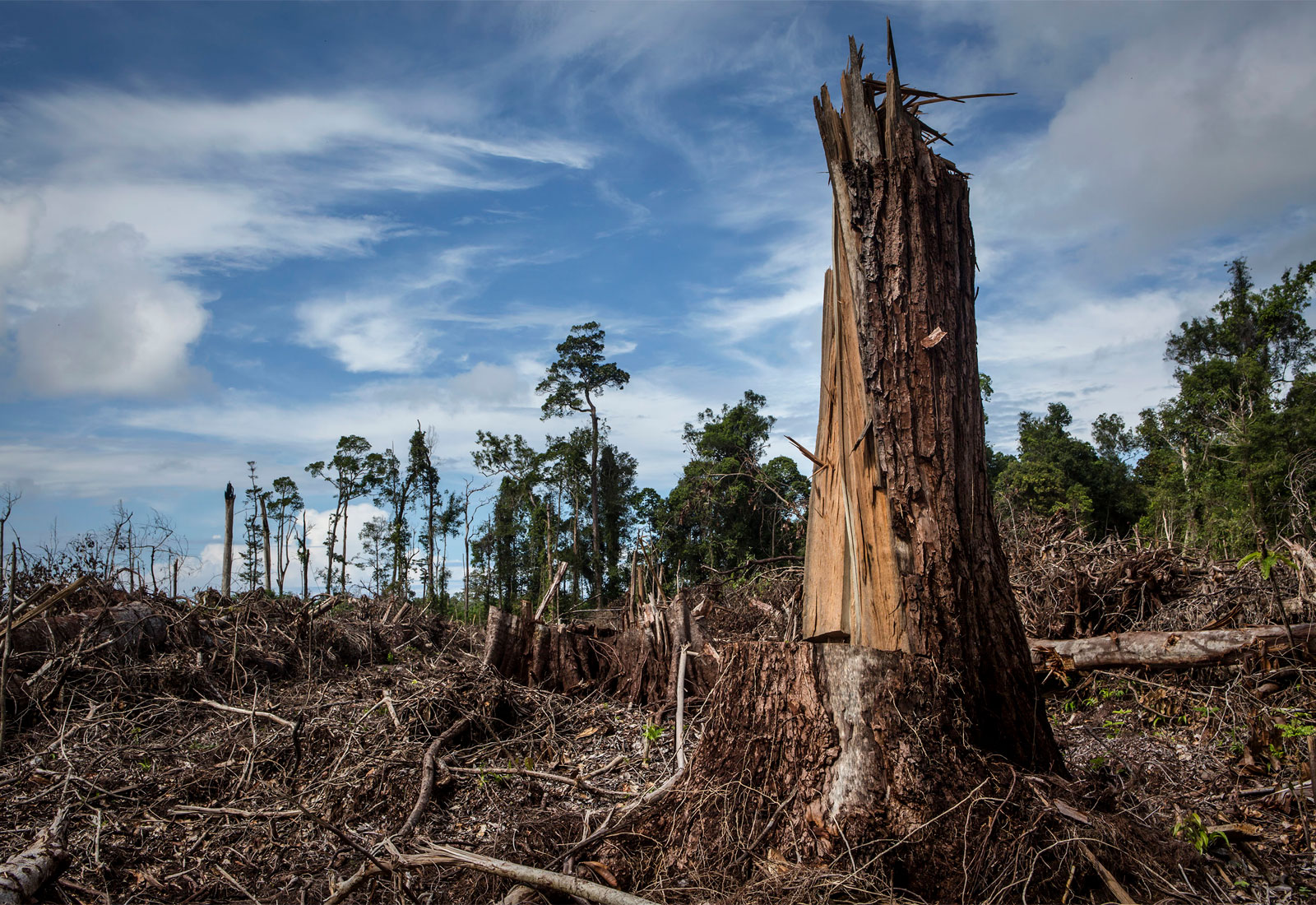 3 · Environment
3 · EnvironmentCauses: Agriculture, urbanization.
Consequences: Loss of biodiversity, soil erosion.
Explanation: The massive removal of trees and forests, usually for farming, logging, or urban growth. It destroys animal habitats, reduces biodiversity, and causes soil erosion and climate imbalance.
 4 · Resources
4 · ResourcesCauses: Overexploitation, excessive consumption.
Consequences: Water and energy scarcity, economic crisis.
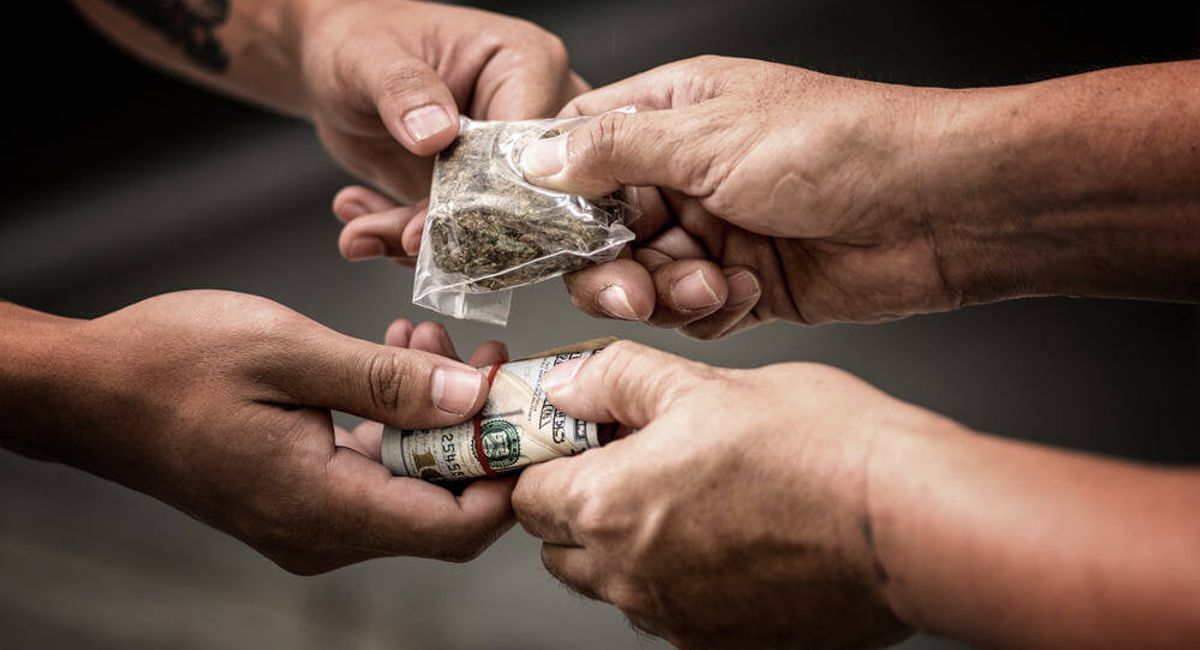 5 · Society
5 · SocietyCauses: High demand, poverty.
Consequences: Violence, addictions.
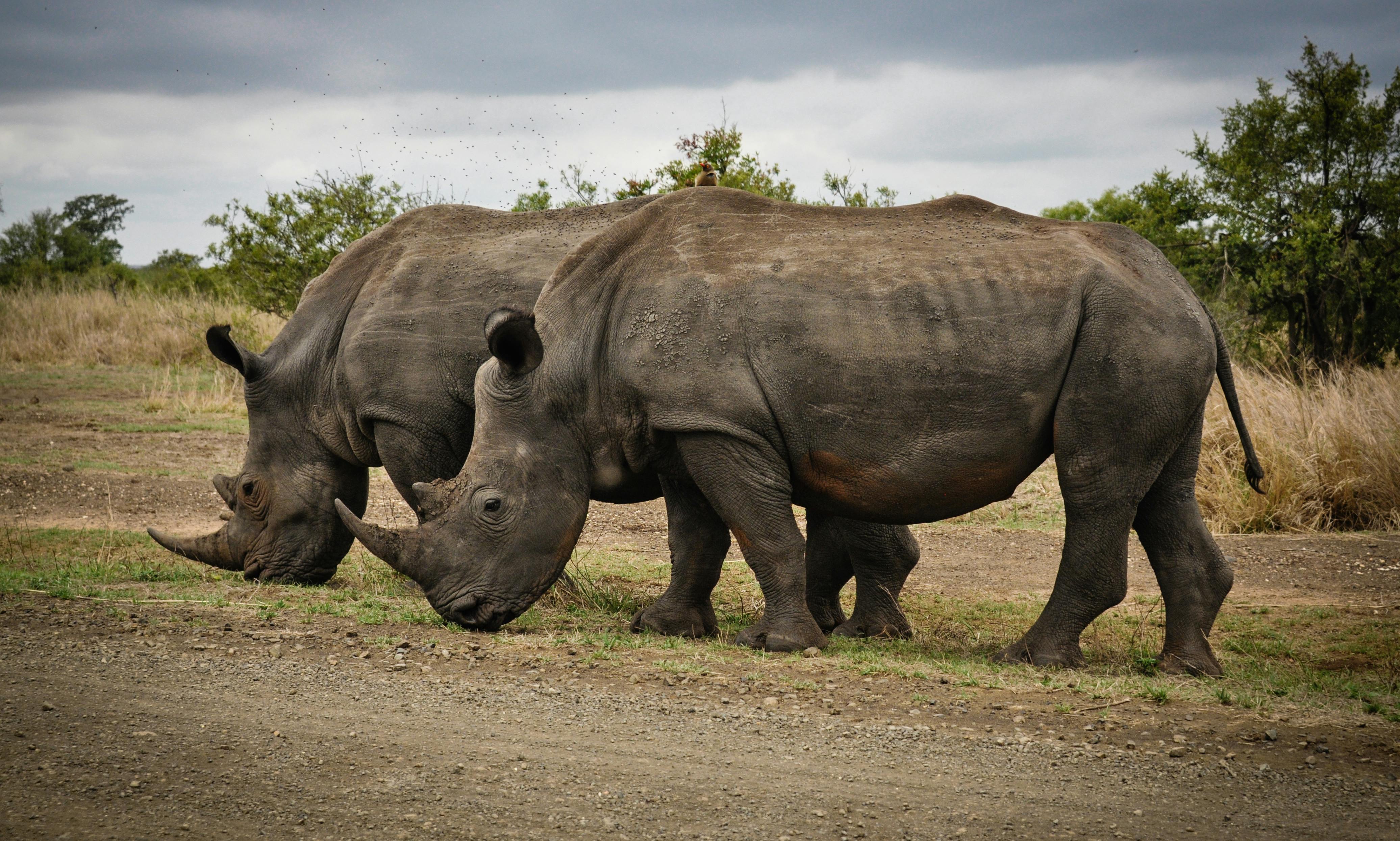 6 · Biodiversity
6 · BiodiversityCauses: Hunting, habitat destruction.
Consequences: Loss of biodiversity, ecosystem imbalance.
 7 · Humanitarian
7 · HumanitarianCauses: Droughts, armed conflicts.
Consequences: Mass hunger, mortality.
 8 · Climate
8 · ClimateCauses: Greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation.
Consequences: Melting glaciers, extreme weather.
 9 · Governance
9 · GovernanceCauses: Lack of control, greed.
Consequences: Inequality, loss of trust.
 10 · Climate
10 · ClimateCauses: Excess CO₂, methane.
Consequences: Global warming, climate changes.
 11 · Health
11 · HealthCauses: Sexual transmission, contaminated blood.
Consequences: Opportunistic diseases, death.
 12 · Economy
12 · EconomyCauses: Overprinting money, high production costs.
Consequences: Loss of purchasing power, poverty.
 13 · Waste
13 · WasteCauses: Excess waste, poor waste management.
Consequences: Soil pollution, bad odors.
 14 · Industry
14 · IndustryCauses: Industrial demand, economic growth.
Consequences: Deforestation, water pollution.
 15 · Urbanization
15 · UrbanizationCauses: Rapid urbanization, real estate speculation.
Consequences: Loss of green areas, urban saturation.
Explanation: The uncontrolled construction of too many houses or buildings in one area. It reduces green spaces, increases traffic and pollution, and often leads to overcrowded cities with poor living conditions.
 16 · Demography
16 · DemographyCauses: High birth rates, low mortality.
Consequences: Food and water shortages, unemployment.
Explanation: When the number of people grows faster than the resources available. It puts pressure on food, water, and jobs, leading to poverty, shortages, and environmental damage.
 17 · Society
17 · SocietyCauses: Inequality, corruption.
Consequences: Protests, violence.
 18 · Society
18 · SocietyCauses: Unemployment, inequality.
Consequences: Hunger, social exclusion.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-108875899-5a6f943cc5542e0036df7b25.jpg) 19 · Environment
19 · EnvironmentCauses: Traffic, industries.
Consequences: Stress, hearing loss.
Explanation: Excessive or disturbing sounds from traffic, airplanes, or industries. Constant exposure affects mental health, increases stress, and may cause hearing loss.
 20 · Animal Welfare
20 · Animal WelfareCauses: Abandonment, lack of population control.
Consequences: Spread of diseases, attacks.
 21 · Safety
21 · SafetyCauses: Poverty, unemployment.
Consequences: Insecurity, violence.
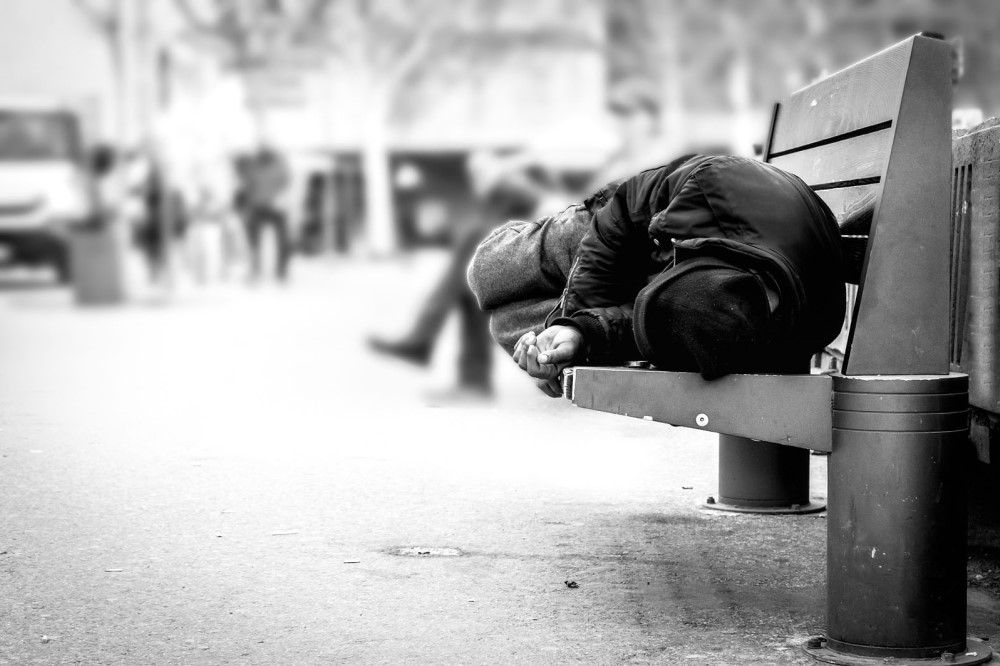 22 · Society
22 · SocietyCauses: Poverty, job loss.
Consequences: Social exclusion, health problems.
Explanation: People who live without stable housing, often sleeping on streets or shelters. Causes include poverty, unemployment, or family issues, and consequences are social exclusion and serious health problems.
 23 · Atmosphere
23 · AtmosphereCauses: CFC emissions, pollution.
Consequences: Skin cancer, crop damage.
 24 · Economy
24 · EconomyCauses: Economic crisis, lack of education.
Consequences: Poverty, crime.
 25 · Environment
25 · EnvironmentCauses: Chemical waste, garbage.
Consequences: Diseases, death of aquatic life.
Explanation: The contamination of lakes, rivers, and oceans with chemicals, plastics, and waste. It harms marine animals, spreads diseases, and reduces access to safe drinking water for communities.
 26 · Biodiversity
26 · BiodiversityCauses: Trade of skins/ivory, lack of control.
Consequences: Species extinction, ecological imbalance.